Optimal f is a fixed fractional money management method that applies an anti-martingale approach. This method is more advanced than the 2% Rule and seeks to set the optimal position size for each trade. Secure f is a more conservative application of Optimal f which is a very aggressive form of money management.
Ralph Vince was one of the original Turtle Traders. He is a math guy who has written several books on money management in trading. He is the architect of both the Optimal f and Secure f Money Management Methods. His method is responsible for Larry William’s championship run, turning a $10,000 account into $1.1 million in just 1 year.
Optimal f
Optimal f is a money management strategy used to maximize the system performance by finding the best percent of capital to use in each trade. It determines which percent of equity would have yielded the highest return based on a sequence of past trades. The concept comes from the Kelly formula which estimates the percentage of your capital to trade when the amounts won or lost are not equal:
f = ((b+1)p – 1))/b
b = Ratio of the size won on a winning bet to the size lost on a losing bet
p = Probability of a winning bet
A simple example would be if you had three bets — two winners and one loser (1, 1, zero) — and you made or lost equal amounts:
f = ((1+1)0.666-1)1 = 0.33333
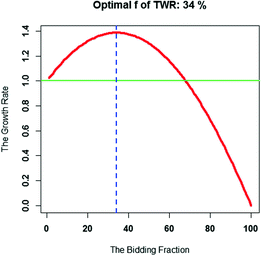
This formula solves for f. This formula is applicable when there are only two outcomes. For traders, there are many outcomes. Vince introduces optimal f, and to find the value of optimal f, we need to maximize what Vince calls terminal wealth relative (TWR). The problem can be formulated thus:
TWR(f) -> max
where TWR(f)=(HPR1(f))((HPR2(f))(…(HPRn(f))
HPRi(f)=1+(f((-Return on the trade i)/(Return on the worst losing trade))
HPR = Holding period return
N = (F*Equity/Risk) / price
The equation for finding the position size under optimal f
F is the factor based on the basis of historical data, and the risk is the biggest percentage loss that you experienced in the past. Using these numbers and the current price, you can find the number of contracts you need to trade.
If your account balance is $25,000, your biggest loss was 40%, your F is calculated to be 30%, and your looking to trade a stock that is trading at $25 per share, so you should buy 750 shares.
The Optimal F number itself is a mean based on historical trade results. The risk number is also based on past returns, so this method only kicks in after you have some trade data. Also, you need to set up a spreadsheet to calculate it. Some traders only use Optimal F in certain market conditions, in part because the history changes each time a trade is made, and that history doesn’t always lead to usable numbers.
Secure f
To formulate the problem solved by secure f, we add a constraint into the calculation of optimal f. The constraint may reflect the acceptable maximum drawdown (and/or other characteristics). This is a more conservative strategy that has the benefit of finding the percent of equity invested in every trade that would have yielded the highest possible return subject to the acceptable maximum drawdown. Let us reformulate the problem of finding optimal f by adding the drawdown constraint:
TWR(f) —> max subject to Maximum drawdown(f) is less than or equal to acceptable maximum drawdown set by trader
This formulation of the problem is such that its solution will maximize TWR and guarantee that the drawdown when running the system on past data does not exceed the amount defined by the trader — value D. This value is referred to as acceptable maximum drawdown. (This could be a trade or equity drawdown or other risk measure, or several risk measures at the same time. There could be a constraint that includes a measure of volatility. Other constraints can be taken into account in the same way just by adding more constraints.
If trading the Optimal f method is like driving without brakes, the Secure f method allows you to brake only if the car gets to a certain speed.
CONCLUSIONS
Secure f method offers you the ability to maximize the return subject to the level of risk you are willing to assume. Secure f can be a conservative or aggressive strategy, depending on the level of acceptable maximum drawdown you select. This level can be set to match your risk tolerance. The secure f strategy can be applied to both mechanical and non-mechanical trading and to increase profitability in any market.
This is just a brief introduction of Optimal f and Secure f. If you are mathematically inclined, you absolutely need to read Ralph’s books to explore all the details of this mathematical model.
Optimal f seems to work best when the end goal is decided like in the Trading Championship, and Secure f is the preferred method by traders wanting to implement it throughout their trading careers.
Recommended Ralph Vince Books
Portfolio Management Formulas: Mathematical Trading Methods for the Futures, Options, and Stock Markets
Explores two neglected mathematical tools essential for competing successfully in today’s frenzied commodities markets: quantity, which shows the proper
amounts a trader should trade for a given market and system, and intercorrelation of returns (diversification), which shows not only which markets and systems to trade,
but how to diversify with respect to trading the right quantities for each market.
The Mathematics of Money Management: Risk Analysis Techniques for Traders
The Mathematics of Money Management substitutes precise mathematical modeling for the subjective decision-making processes many traders and serious investors depend on.
Step-by-step, it unveils powerful strategies for creating and using key money management formulas–based on the rules of probability and modern portfolio theory–that
maximizes the potential gains for the level of risk you are assuming.
The New Money Management: A Framework for Asset Allocation
In this groundbreaking new book, Vince takes aquantum leap forward to provide investment professionals with aproven new approach to portfolio management
that overturns nearly ahalf-century of accepted wisdom about asset allocation and moneymanagement.
The Handbook of Portfolio Mathematics: Formulas for Optimal Allocation & Leverage
Vince introduces a leverage-space portfolio model, tweaks it for the drawdown probability, and delivers a superior model. He even provides equations
to maximize returns for a chosen level of risk. So if you’re serious about making money in today’s markets, buy this book. Read it. Profit from it.
The Leverage Space Trading Model: Reconciling Portfolio Management Strategies and Economic Theory
In The Leverage Space Trading Model, Vince offers a groundbreaking contribution to the literature that builds on a lifetime of expert analysis to deliver
not only a superior new portfolio model, but takes the entire discipline of portfolio management to a new level.
Risk-Opportunity Analysis
This Second Edition is presented for the non-mathematician (though the underlying math is provided for those who are interested), and not only gives reason to reconsider
the bases we assess gambling and investing situations, but reveals this magnificent, innate ability we possess.







